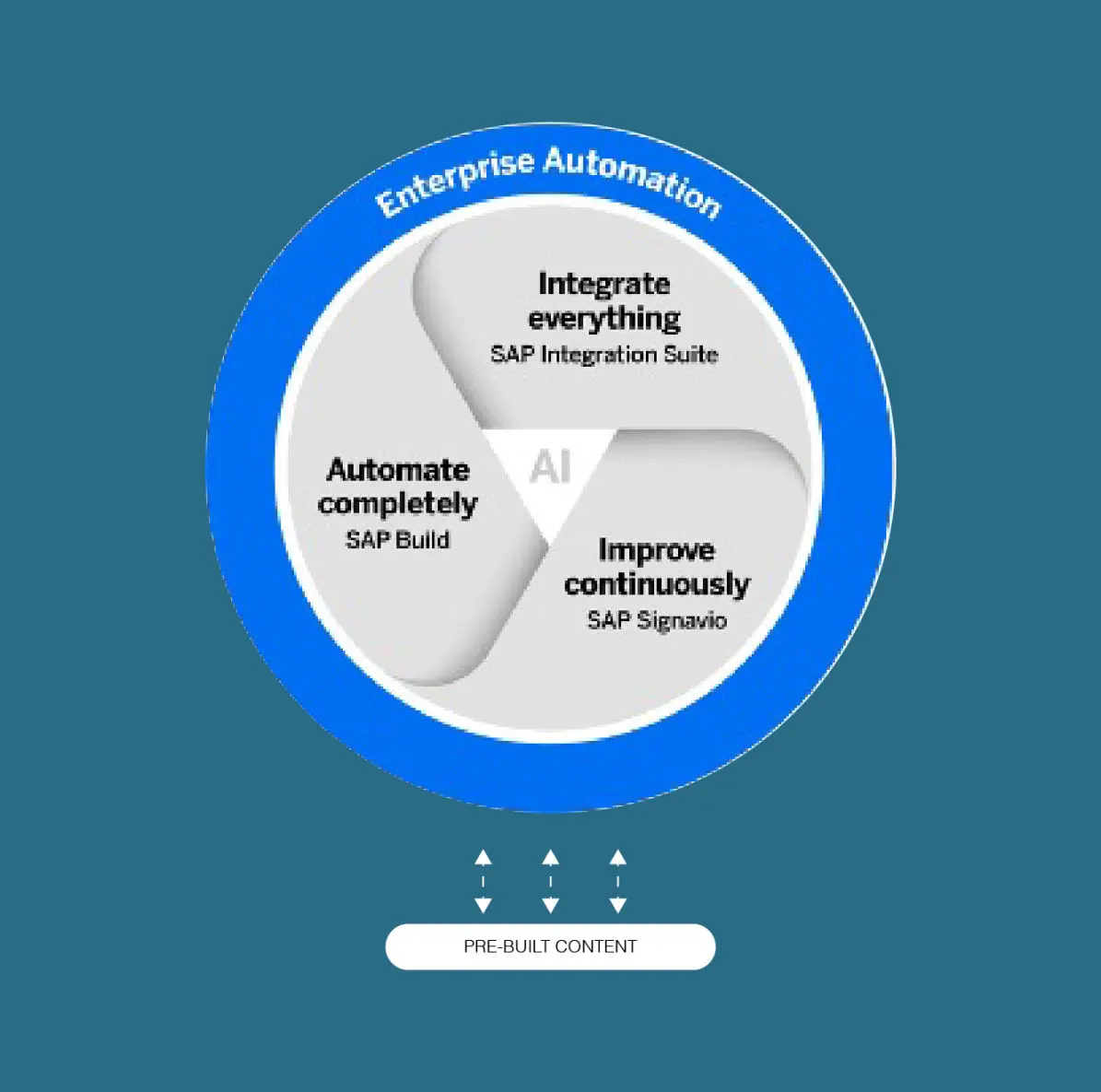
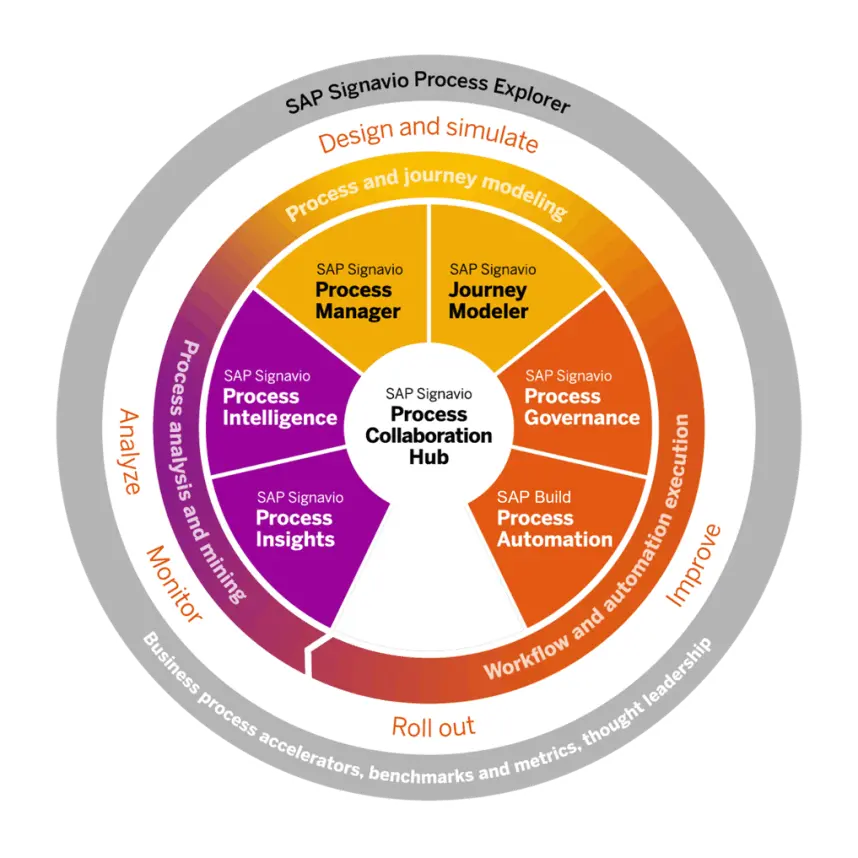
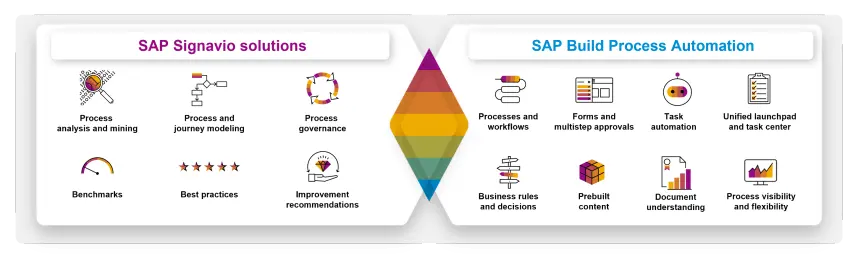
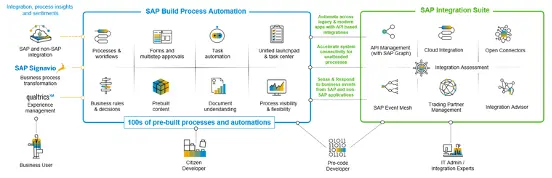
Automating SAP processes can bring significant benefits, but it also poses several challenges. Below are the most common challenges associated with SAP automation:
- Complexity of SAP Systems: SAP systems are often complex and highly customized to fit specific business processes. Automating these processes requires a deep understanding of SAP functionalities, modules, and integration points, which can be challenging for automation engineers.
- Variability in SAP Environments: SAP environments can differ significantly between organizations, versions, and configurations. This variability adds complexity to automation efforts, as scripts and workflows may need to be customized or adapted to accommodate differences in system setups.
- Lack of Standardization: In some cases, SAP implementations may lack standardization across different business units or regions within an organization. This lack of standardization can make it difficult to develop reusable automation scripts and workflows, leading to increased development time and effort.
- Data Complexity and Volume: SAP systems typically handle large volumes of data across multiple modules and applications. Automating processes that involve data extraction, transformation, and validation can be challenging due to the complexity and volume of data involved.
- Integration with External Systems: Many SAP processes involve interactions with external systems, such as third-party applications, databases, or APIs. Integrating SAP automation with these external systems can be complex and may require custom development or middleware solutions.
- SAP Security and Authorization: SAP systems often have strict security and authorization requirements to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Automating SAP processes while adhering to security policies and access controls can be challenging and requires careful planning and implementation.
- Change Management: SAP systems are subject to frequent changes, including software updates, configuration changes, and business process changes. Managing these changes and ensuring that automation scripts remain up-to-date and compatible with the latest system configurations can be challenging.
- Performance and Scalability: Automating large-scale SAP processes may put a strain on system resources and impact performance. Ensuring that automation scripts are optimized for performance and scalability requires careful design and testing.
Addressing these challenges requires technical expertise, domain knowledge, and effective collaboration between business users, IT teams, and automation engineers. By understanding these challenges and implementing best practices, organizations can overcome obstacles and realize the full benefits of SAP automation.